What are the consequences of playing video games? Do violent video games cause more violence among players? Are video games just a waste of time or does playing them bring any benefits?
The World Of Video Games
Video games can be defined as interactive electronic games that essentially aim to entertain players. According to Quwaider et al. (2019), video games allow players to access virtual 2D or 3D environments within specific rules and conditions that differ from game to game.
Video games can either be played offline or online. The latter is done via a live network connection using a console, PC or portable device. Moreover, video games can even be played in a massively multiplayer online role-playing (MMORP) environment. These are, by design, games run in real-time that are highly social and competitive – calling for a high level of commitment and cooperation amongst players.
There are different categories of video games, some more popular than others. From action to sports games, strategy, shooting, racing or adventure, there are many different types of games that require different skills from players. While some gamers need to play strategically in the long run, others need to predict opponents’ moves or know when is the right moment to slow down the car and go for a perfect curve.
Video Games Are Evolving And Looking Like Real Games
Just like other new technologies, the techniques, playability, levels, requirements or the ability of video games to constantly challenge and have players’ attention have been developing. A couple of years ago, 3D games were barely a thing and these days they are becoming the new normal.
As of February 2019, Germany was the country where people spent more time on average playing video games (7.98h/week), followed by the US (7.61h/week) and Singapore (7.54h/week). The global average at the time was (7.11h/week).
As the video game industry is expected to grow, the concerns regarding those who play video games them grow as well. Especially, because among the audience of video game players, many are children who are still forming their personality. So it is important to carefully study their impact on the behaviors of players as they play and after they do it.
Since our personality influences how we think and behave, the way a player responds to a video game depends on how they interpret it in their mind. That’s why some studies say neurons in the human body deal with the effects that happen when playing online (in real-time, with other players) video games just as the same dealing with the effects in the real world. Let’s take a look at the consequences of playing video games.
The Positive Effects Of Playing Video Games
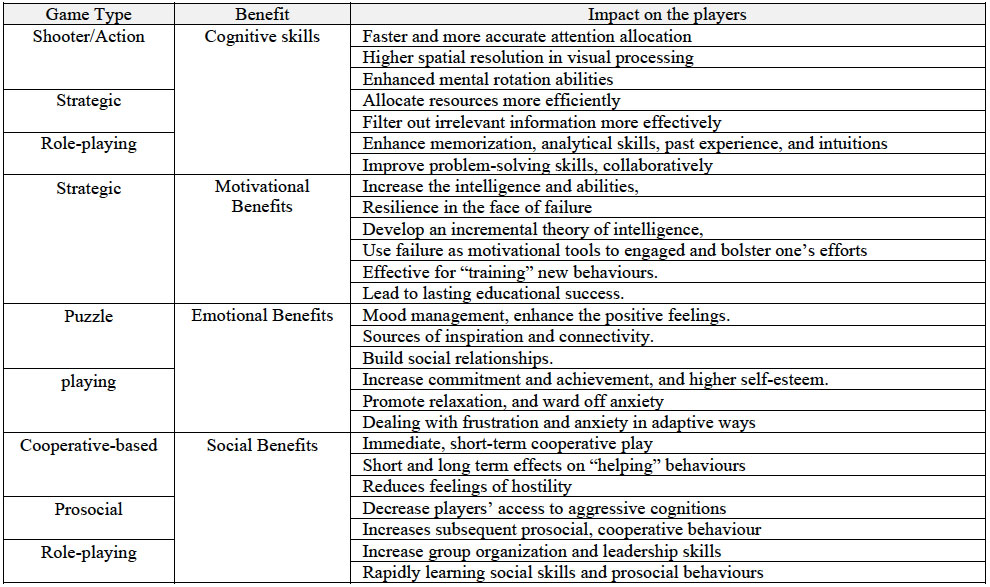
A literature review made by Quwaider et al. on the topic resulted in a comprehensive table connecting the different types of videogames with their (negative and positive) effects. Of course, both positive and negative impacts will depend on variables such as the personality of individuals, how long they play for or how often or their emotional balance and sleep time.
When it comes to the benefits of playing video games, action/shooter, strategic and role-playing games seem to be linked with improvements on vision, spatial and problem-solving skills, the ability to allocate resources more efficiently or to filter relevant information more efficiently.
By their turn, strategic games seem to be connected with resilience in the face of failure while puzzle and playing games enhance positive feelings, increase self-esteem and promote relaxation.
Hence, cooperative-based games, as well as prosocial and role-playing games have strong ties with social benefits. They reduce feelings of hostility, decrease cognitive aggression, increase cooperative behaviors and promote the quick learning of social skills.
The Negative Effects Of Video Games: From Anxiety To Depression And Reckless Driving
Despite the benefits above, and as we’ve been briefly discussing throughout this piece, playing video games also has negative consequences. For instance, within sports games like FIFA or Fight Night Round, players can experience anxiety regarding the outcome of the game while feeling joy or pride in the end.
When it comes to racing games, playing Gran Turismo or Need For Speed can increase the chances of taking riskier real-life decisions in the pursuit of similar sensations players. In fact, a study by Draghici et al. (2012) found a link between playing such video games and increased reports of several risky driving habits – like speeding, tailgating or weaving in traffic. Automobile accidents, greater willingness to drink and drive or being stopped more often by the police were other consequences of players’ sensation seeking and rebelliousness.
Moreover, a study conducted on Norwegian teenagers showed video game addiction was positively linked with internal behavior problems like depression and conduct problems. Another study found a significantly increased risk of depression among 13-17-year-olds consistently playing and using their phones for texting and scrolling social media between 10-12 pm and 18-22-year-olds doing the same between 2-6 pm.
The “Do Violent Video Games Cause Violence” Debate
According to the summary table from Quwaider et al, fighting games such as Tekken or Mortal Combat have a higher risk for hostile and aggressive behaviors. This is also the case with shooting games like Counterstrike or Hallo – the latter which can push for competitive (inter-group) or cooperative (intra-group) attitudes.
Other studies published on Media Psychology or Elsevier have also established links between the increase of external behavior problems – such as more aggressive and violent behaviors – with playing first-person shooters games and other types of violent games. The first study suggests aggressive cognitions and feelings occur independently of how technologically advanced the graphics are or the extent to which one feels immersed in the game. The second study had opposite results as it concluded more realistic games led to more physically violent intentions.
Further, multiplayer online role-playing games, often offering a more immersive reality, were found to be predictive of external behavioral difficulties like aggression or delinquency.
Some Studies Show No Connection Between Playing Video Games And Human Behaviors Or Violence
That’s right. And that’s also how science works – constantly questioning and searching for the truth. The fact is that much of the findings we’ve been discussing throughout this piece are not the same ones found, for instance, a study from the University of New York showed no significant connection between the realism of the video games and the behavior of players.
Another study also demonstrated that playing a game containing the realism behavior of death did not lead to increases in violent behaviors. Hence, a 2016 study that analyzed kids aged 6-11 also showed no relationship between the amount of time spent playing video games and the kids’ emotional and mental health, nor in the way they behaved.
Playing Too Much Video Games, Even If Not Violent Ones, Meaning Less Time Doing Other Things
By giving time to creating and developing on a new identity in-game, users are “distracted from real-world challenges and opportunities” and consequently withdraw from previous life roles and routines. This has often been called the “Internet paradox,” where communication technology may, in fact, lead to greater isolation and loneliness.
Using the words of Scott and Armstrong (2013), playing massively multiplayer online role-playing games (MMORPGs) can impact the psychosocial well-being of adolescents and young adults; however, only tentative statements can be made about the nature of this impact – as we’ve understood before, due to contradictory conclusions that were also found.
It looks like without knowing in detail the type of game and the personality and history of gamer, drawing conclusions upon the impact is hard and can be misleading. While most studies conclude playing video games is somehow connected to the player’s personality and behaviors; others claim video games have no impact on the players – and support their claims in the type of game played and the amount of time spent playing.
Nonetheless, it seems hard to ignore the impact of video games on human behavior. In this respect, Quwaider et al. (2019) said, most of the research that denied the existence of the impact of video games relies on a small number of participants or weak evidence.
There is, however, one thing that can be generically assumed: playing video games for excessive periods of time means spending one of our most scarce resources: time. There’s still a real world outside the screens and many different ways of getting entertained while doing real-life socializing, getting fit and healthy or discovering new places.
Photo by Alexander Andrews on Unsplash

